Gynecomastia is a condition where unusual breast gland tissue grows in men at any age. Hormonal imbalances can be the reason in males and newborns. It can also be caused by hormone-related disorders such as tumors, malnutrition, renal, liver, or thyroid illness, or pharmacological therapy.
What is Gynecomastia?
Gynecomastia, or an increase in male breast volume, is a condition that most commonly occurs during times of hormonal change, such as at birth, adolescence, and old age. Obesity, steroid use, use of certain other pharmacologic agents, and medical conditions such as hypogonadism, liver and kidney failure are among the many etiologies for gynecomastia. However, the majority of patients have idiopathic (unknown cause) gynecomastia.
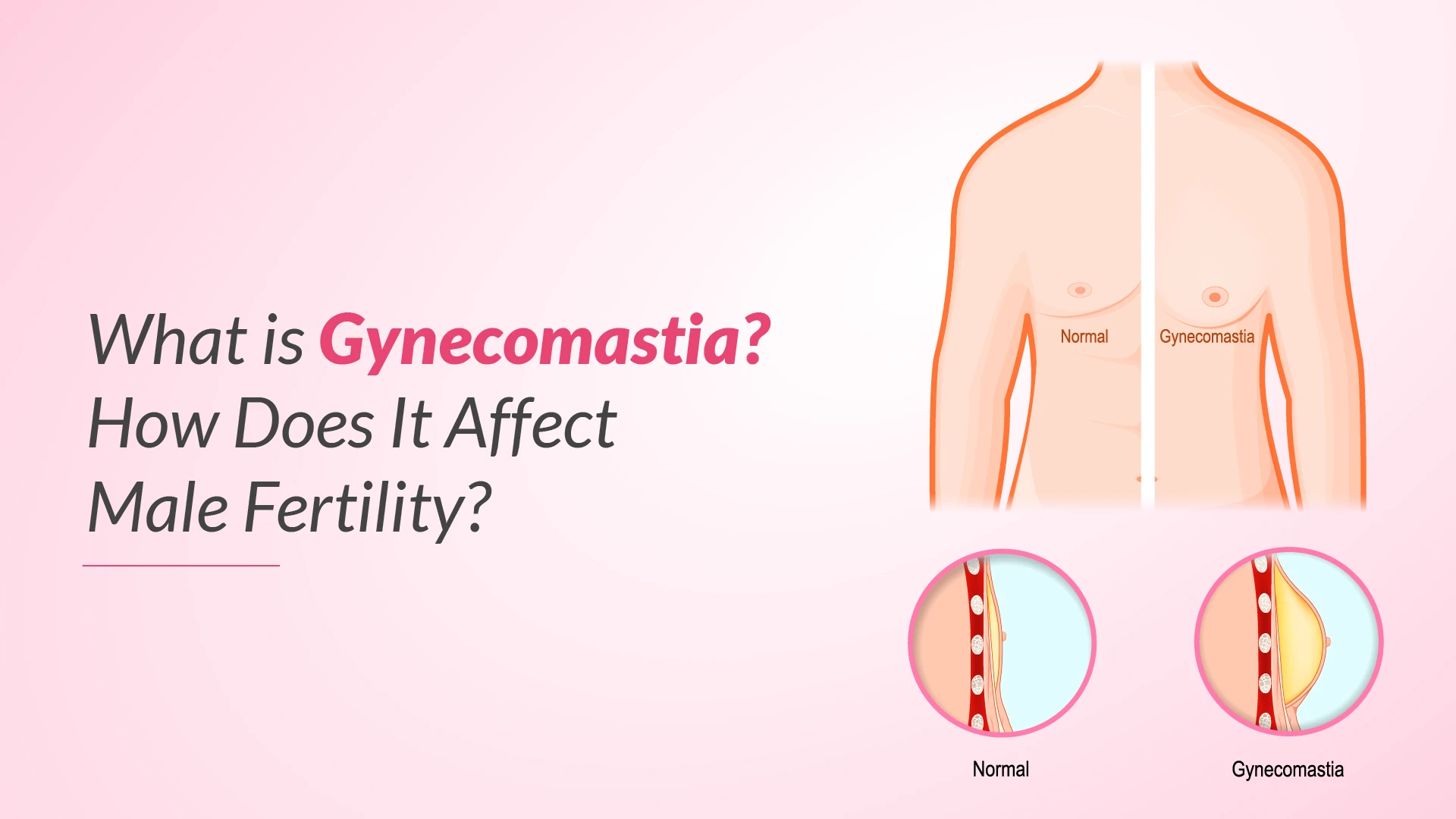
How Does Gynecomastia Look and Feel?
Gynecomastia usually appears and feels like a button-sized growth beneath your nipple. You may notice this as a breast lump or feel it when you push on the region. The lump may move freely inside the breast tissue and be sensitive to touch. The nipples and breasts may seem swollen and painful. Breast lumps and enlargements may develop in one or both breasts, and they may be rubbery or firm.
Find hope and help – learn more about our male infertility treatments now!
Causes of Gynecomastia
It results from an imbalance of the hormones estrogen and testosterone. This imbalance usually happens naturally in infants, aged 0 to 3 weeks, in boys, where the puberty generally occurs between the ages of 10 and 17, and in elderly males experiencing it more frequently after 50 years.
Birth
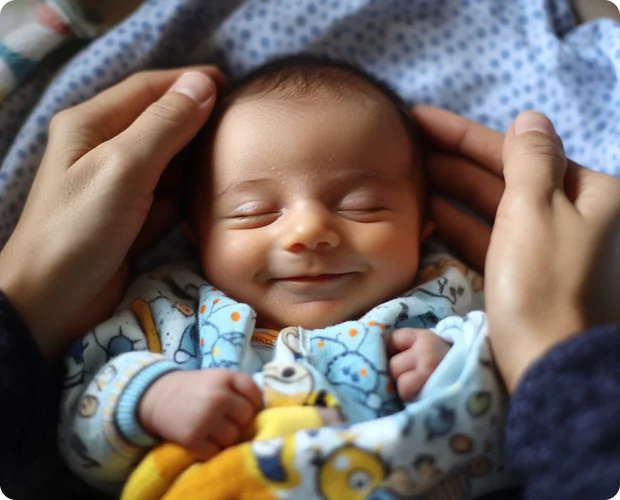
Gynecomastia in neonates is induced by the mother’s estrogen, which passes through the placenta and remains in the baby’s blood for a period after delivery. More than half of male newborns are born with larger breasts; the enlarged breast tissue normally disappears within 2 to 3 weeks following delivery.
Puberty
Gynecomastia is frequent during adolescence owing to hormonal changes associated with puberty, such as a decrease in testosterone and an increase in estrogen. It affects one or both breasts in around half of all boys aged 12 to 16.
Late Adulthood
It is more frequent in older men owing to excess body fat, which increases estrogen production. Other causes of gynecomastia in older individuals include hormonal imbalances, medicines, thyroid disorders, and pituitary gland tumors.
Also read: Role of Hormones in Fertility
Impact on Male Fertility
Gynecomastia is characterized by aberrant growth of benign ducts and supporting tissue, resulting in breast growth or enlargement (benign). It can also create a subareolar lump and occasionally breast tenderness, and it is not associated with fertility issues in most cases.
Hormonal Imbalance and Sperm Production
The hormone estrogen promotes glandular tissue development while also suppressing testosterone release. Other chromosomal or hormonal abnormalities, such as hair loss on the face or body, have been observed. A lower-than-normal sperm count is also associated with gynecomastia.
Reduced Testosterone Levels
In addition to increased estrogen production, decreasing testosterone levels can produce a rise in the estrogen to androgen ratio, resulting in gynecomastia.
Associated Hypogonadism
Conditions that reduce the body’s testosterone production have been related to gynecomastia. Some instances include Klinefelter syndrome and pituitary insufficiency.
Impaired Libido and Sexual Function
Patients with gynecomastia are more prone to report sexual issues, including low sexual desire due to low levels of testosterone, reduced frequency of intercourse, serious erectile dysfunction, delayed ejaculation, and reduced ejaculate volume.
Psychological Stress and Anxiety
Gynecomastia can have a severe psychological impact; men may feel anxious when they first observe glandular tissue development. It can have a negative impact on self-esteem, particularly in teenage boys.
Long-Term Fertility Implications
Gynecomastia is prone to arise when a hormonal imbalance occurs and affects testosterone levels. Gynecomastia and hypogonadism will occur in men with Klinefelter syndrome. The likelihood of experiencing infertility increases if hypogonadism and gynecomastia coexist in such a situation. The illness is commonly identified around adolescence and can lead to consequences such as poor sperm count and infertility.
Also Read: AndroMax: Ferty9’s Solution for Enhancing Male Fertility
Treatment for Gynecomastia
If gynecomastia is left untreated, it disappears with time. On the other hand, treatment may be required for any underlying medical issue that causes gynecomastia. If you take a medication that may be the cause of gynecomastia, consult your doctor about the other safer choice of drugs. Treatment options include drugs used to treat breast cancer and surgeries to remove extra breast tissue, such as liposuction and mastectomy.
Suggested Read: Why Male Infertility Rates Are Rising in India
Managing Gynecomastia to Improve Fertility
The sex hormone testosterone regulates characteristics such as muscle mass and body hair. Estrogen regulates several features, including breast development. Gynecomastia can be caused by an imbalance in estrogen and testosterone levels. This can lead to erectile dysfunction, decreased sperm quality, muscle loss, gynecomastia, infertility, and depression. Excess body fat can also lead to decreased testosterone levels, so having a balanced diet, especially testosterone-boosting foods, and physical activity can improve the levels of the hormone. Testosterone replacement treatment (TRT), which includes injections, skin gels, and patches, can help you increase your testosterone levels, thus improving fertility.
Also Read: Top Vitamins for Boosting Fertility
Conclusion
Having enlarged breasts may be distressing and embarrassing for those who have gynecomastia. But you can feel better and more confident by seeking regular medical attention, seeking counseling, connecting with friends and family, and interacting with others who share your condition.