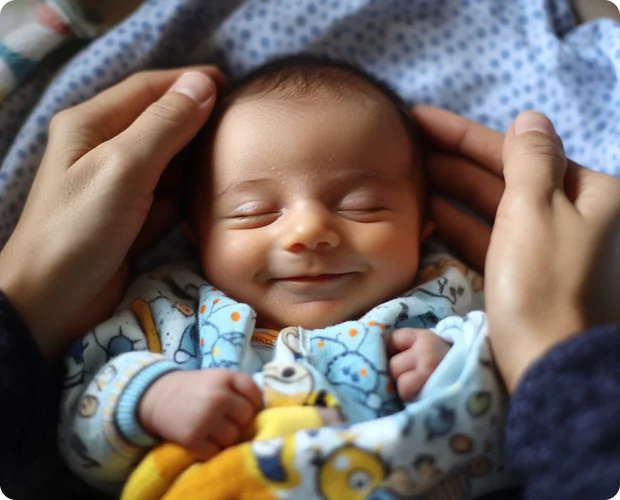
The fertility ratio is a measure that compares the reproductive potential of males and females within a population. It is a crucial demographic indicator that provides insights into overall fertility levels and helps understand the dynamics of population growth or decline. The fertility ratio considers various factors, including biological, social, and environmental influences, to assess the relative fertility rates between the two genders.
In essence, the fertility ratio aims to answer the question: Is male infertility higher or lower than female infertility? This question has significant implications for understanding population trends, family planning, and reproductive health policies.
Also read: Exploring the Decline in India’s Fertility Rate
Fertility in Demography
Trends in Fertility in Population
Fertility rates have undergone significant changes over time, influenced by various societal, economic, and cultural factors. Historically, high fertility rates were prevalent due to the need for larger families to support agricultural and labor-intensive economies. However, with industrialization, urbanization, and women’s empowerment, fertility rates have generally declined in many parts of the world.
Impact of Demographic Changes on Fertility
Demographic transitions, such as increased access to education, improved healthcare, and changing gender roles, have profoundly impacted fertility patterns. In developed nations, fertility rates have often fallen below the replacement level, leading to concerns about population aging and a declining workforce. Conversely, some developing countries still grapple with high fertility rates, posing challenges to sustainable development and resource allocation.
Suggested Read: Unraveling the Causes behind the Escalating Male Infertility Rates in India
Infertility Rate in Men vs Infertility Rate in Women
The inability of a couple to conceive after one year of unprotected sexual contact is known as infertility. It affects both men and women. According to a report by the World Health Organisation (WHO), approximately 10-15% of couples worldwide experience infertility issues. While the prevalence of infertility varies across regions, the general trend suggests that male and female infertility rates are comparable.
Male infertility accounts for around 40% of infertility cases, while female infertility contributes to approximately 40% of cases. In the remaining 20 % of cases, infertility is attributed to a combination of factors involving both partners or unexplained causes.
Related Read: Did You Know 1 in 6 People Globally Are Affected by Infertility?
Factors Contributing to Infertility in Men and Women
Infertility can arise from a multitude of factors affecting both men and women. Understanding these factors is crucial for addressing fertility challenges and improving reproductive outcomes.
For men, some of the key factors contributing to infertility include:
- Low Sperm Count or Quality: This can be influenced by genetic factors, lifestyle choices (e.g., smoking, alcohol consumption), environmental exposures, or underlying medical conditions.Suggested Read: How to increase sperm count and motility
- Hormonal Imbalances: Conditions like hypogonadism or pituitary gland disorders can disrupt the production of hormones essential for sperm production and sexual function.
- Anatomical Abnormalities: Structural issues in the male reproductive system, such as varicoceles (enlarged veins in the scrotum) or obstructions in the vas deferens, can impair fertility.
For women, some common factors contributing to infertility include:
- Ovulatory Disorders: Conditions like hypothalamic amenorrhea or polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) can disrupt ovulation, making it difficult to conceive.
- Fallopian Tube Blockages or Damage: Infections, endometriosis, or previous pelvic surgeries can cause scarring or blockages in the fallopian tubes, preventing the egg from traveling to the uterus.
- Uterine or Cervical Abnormalities: Structural abnormalities in the cervix or uterus, such as uterine fibroids or polyps, can interfere with implantation or fertilization.
Fertility Percentage in Different Age Groups
Age-Related Changes in Female Fertility Rate
A female’s fertility is closely tied to her age, with the peak fertility period typically occurring in the late 20s and early 30s. As a woman grows older, her fertility gradually declines due to a reduction in ovarian reserve and egg quality.
- Women under 30 have the highest fertility rates, with approximately a 20-25% chance of conceiving each month.
- Between the ages of 30 and 35, fertility rates start to decline, with a monthly chance of conception around 15-20%.
- After the age of 35, fertility rates drop more rapidly, with a 10-15% monthly chance of conception.
- By the age of 40, a woman’s fertility rate is significantly lower, with only a 5% monthly chance of conceiving.
Age-Related Changes in Male Fertility Rate
While male fertility is generally considered less age-dependent than female fertility, it is not entirely unaffected by ageing. As men grow older, they may experience a gradual decline in fertility due to various factors.
- In their 20s and 30s, men typically have the highest fertility rates, with a relatively stable sperm count and quality.
- After age 40, a slight decline in sperm quality and quantity may occur, but the impact on fertility is generally less pronounced compared to women.
- By the age of 50 and beyond, the risk of infertility increases due to factors such as decreased sperm motility, lower sperm count, and an increased incidence of genetic abnormalities in sperm.
Also read: The Impact Of Age On Fertility
Effects of Age on Fertility Rates
The age distribution within a population can significantly impact overall fertility rates and demographic trends. In many developed countries, where the average age of childbearing has increased, fertility rates have declined due to the age-related decrease in female fertility.
On the other hand, in some developing nations with a younger population and higher birth rates, the impact of age on fertility may be less pronounced. However, as these populations undergo demographic transitions and experience an ageing population, fertility rates may also decline over time.
Policymakers and medical professionals must consider their respective populations’ age distribution and fertility patterns to develop appropriate strategies for addressing fertility challenges and promoting sustainable population growth.
Find Hope and Solutions for Infertility Problems — Explore Our Comprehensive Services
IVF Treatment
IUI Treatment
ICSI Treatment
Fertility Preservation Service
Blastocyst Culture & Transfer Treatment
Conclusion
The question of whether male fertility is higher or lower compared to female fertility does not have a straightforward answer. While infertility rates are generally comparable between men and women, the factors contributing to infertility and the age-related changes in fertility differ between the genders.
Women experience a more rapid decline in fertility as they age, with the peak fertility period occurring in their late 20s and early 30s. In contrast, men’s fertility tends to decline more gradually with age, and they can remain fertile well into their later years, although with a slightly increased risk of infertility.
Addressing infertility requires a comprehensive approach that considers the unique factors affecting both male and female fertility. Therefore, raising awareness about the importance of reproductive health, promoting early screening and intervention, and providing access to appropriate fertility treatments and support services are crucial.