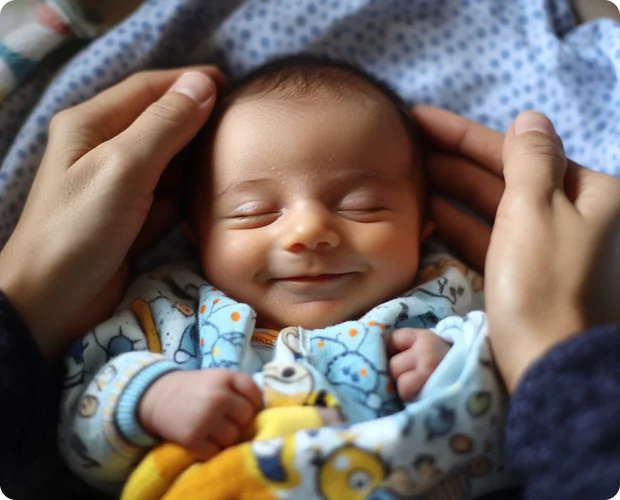
Regenerative medicine has indeed the potential to heal or replace tissues as well as organs that have been damaged by age, disease, or trauma, as well as to normalize congenital defects. Promising preclinical, as well as clinical data to date, support the possibility of treating both chronic diseases as well as acute insults, and for regenerative medicine to abet maladies thus occurring across a wide array of organ systems as well as contexts, including dermal wounds, cardiovascular diseases, and traumas, treatments for certain types of cancer as well as more and more.
The current therapy of transplantation of intact organs as well as tissues to treat organ and tissue failures along with loss that suffer from limited donor supply and often severe immune complications, but these obstacles may indeed potentially be bypassed through the use of regenerative medicine strategies.
The field of regenerative medicine encompasses numerous strategies, that does include the use of materials and de novo generated cells, as well as various combinations thereof, to take the place of missing tissue, effectively thus replacing it both structurally and functionally, or to contribute to tissue healing.
The body’s innate healing response may in fact also be leveraged in order to promote regeneration, although adult humans possess the limited regenerative capacity in comparison with lower vertebrates. This review will indeed first discuss regenerative medicine therapies that have indeed reached the market.
Preclinical as well as early clinical work to alter the physiological environment of the patient by the introduction of materials, living cells, or growth factors either to replace the lost tissue or rather to enhance the body’s innate healing and repair mechanisms will then be reviewed. Strategies for improving the structural sophistication of implantable grafts and effectively making use recently of developed cell sources will also be discussed.
Finally, potential future directions in the field will be proposed. Due to the considerable overlap in how researchers use the terms regenerative medicine and tissue engineering, we indeed group these activities together in this review under the heading of regenerative medicine.
Regenerative Medicine Therapies in the Market
Since the emergence of tissue engineering and regenerative medicine as an industry nearly two decades ago, a number of therapies have indeed received Food and Drug Administration (FDA) clearance or approval and are in fact commercially available. The delivery of therapeutic cells that do directly contribute to the structure and function of new tissues is a principle paradigm of regenerative medicine to date.
- The cells that are made use of in these therapies are either autologous or allogeneic and are rather typically differentiated cells that still do maintain proliferative capacity.
- For instance, Carticel, the first FDA-approved biologic product in the orthopedic field, does make use of autologous chondrocytes for treating focal articular cartilage defects.
- Here, autologous chondrocytes are harvested from articular cartilage, expanded ex vivo, and implanted at the site of injury, thus resulting in recovery compared with that observed by making use of microfracture and mosaicplasty techniques.
- Other examples do include Lviv, which does involve the injection of autologous fibroids treatment in Hyderabad to improve the appearance of nasolabial fold wrinkles.
- Celution, a medical device that extracts cells from adipose tissue-derived from liposuction;
- Epicel, autologous keratinocytes for severe burn wounds; and the harvest of cord blood to obtain hematopoietic progenitor and stem cells.
- Autologous cells do require the harvest of a patient’s tissue, typically thus creating a new wound site, and their use often necessitates a delay before treatment as the cells are culture-expanded.
- Allogeneic cell sources with low antigenicity, for example, human foreskin fibroblasts are made use of in the fabrication of wound-healing grafts (GINTUIT, Apligraf) allowing off-the-shelf tissues to be mass produced, while also thus diminishing the risk of an adverse immune reaction.