Polycystic Ovarian Disease (PCOD) and Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) are two closely related yet distinct conditions that affect women’s reproductive health. While they share some correlations, there are crucial differences between them that are essential to understanding proper diagnosis and treatment. This article aims to shed light on the distinctions between PCOD and PCOS, their causes, PCOS symptoms, and management strategies.
What is PCOD?
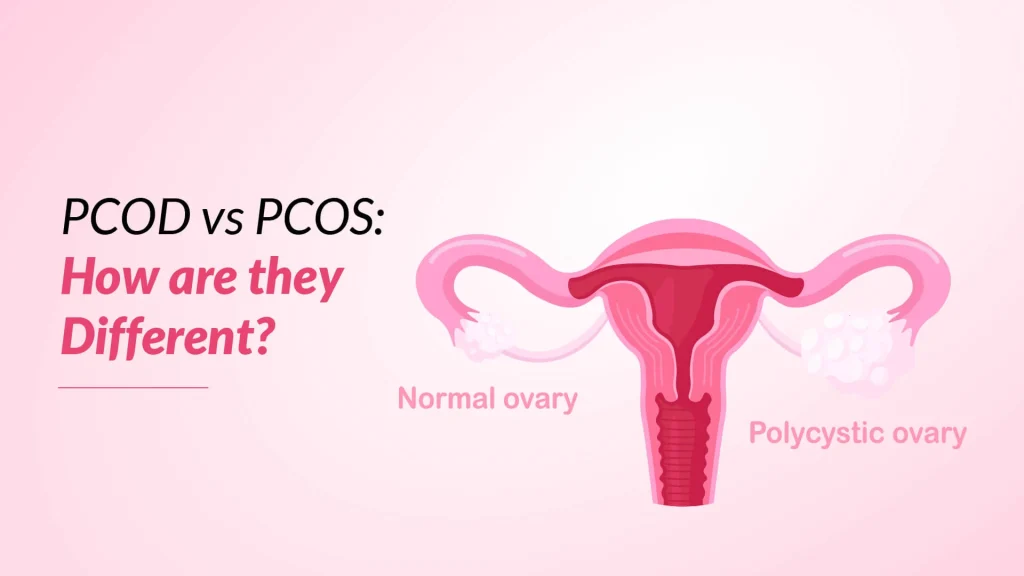
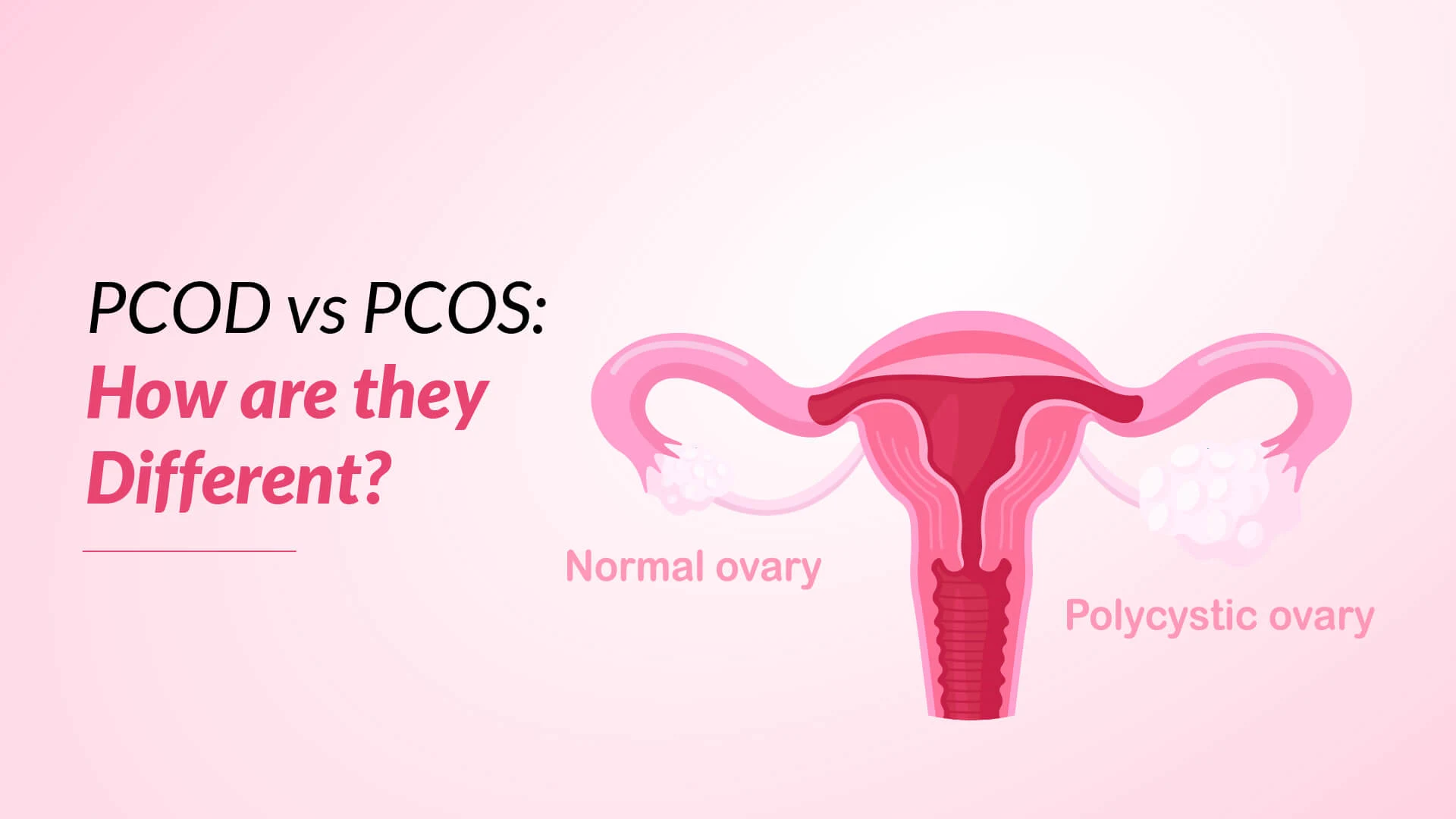
Polycystic Ovarian Disease (PCOD) is a condition characterised by the presence of multiple small fluid-filled sacs (cysts) on the ovaries. These cysts are typically harmless and do not necessarily cause any symptoms or fertility issues. PCOD is often considered a milder form of PCOS, and women with PCOD may or may not experience hormonal imbalances or menstrual irregularities.
Also read: How PCOD does affect fertility?
What is PCOS?
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is a more complex and multifaceted condition that involves hormonal imbalances, ovulatory dysfunction, and metabolic disturbances. Women with PCOS often experience numerous symptoms, including irregular periods, excess hair growth (hirsutism), acne, weight gain, and fertility problems. PCOS is a primary reason for infertility in women. It is also correlated with an increased risk of developing other health problems, such as insulin resistance, type 2 diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases.
Also read: Fertility Challenges In PCOS
Difference Between PCOS and PCOD
To better understand the distinctions between PCOS and PCOD, let’s examine them in a tabular format:
| Aspect | PCOS | PCOD |
|---|---|---|
| Hormonal Imbalance | Significant hormonal imbalances, including elevated levels of androgens (male hormones), insulin resistance, and disrupted ovulation. | Mild or no hormonal imbalances. |
| Cyst Characteristics | Multiple small cysts on the ovaries, often accompanied by an increased ovarian volume. | Multiple small cysts on the ovaries, but ovarian volume may be normal. |
| Menstrual Irregularities | Frequent menstrual irregularities, including oligomenorrhea (infrequent periods) or amenorrhea (absence of periods). | Menstrual irregularities may or may not occur. |
| Diagnostic Criteria | Requires the presence of at least two out of three criteria: irregular periods, elevated androgens, and polycystic ovaries on ultrasound. | No specific diagnostic criteria, but the presence of polycystic ovaries on ultrasound is common. |
| Long-term Health Risks | Increased chances of metabolic disorders, like insulin resistance, type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, and endometrial cancer. | Lower risks of long-term health complications compared to PCOS. |
| Impact on Metabolism | Significant impact on metabolism, including insulin resistance and increased risk of metabolic syndrome. | Milder or no impact on metabolism. |
What are the Causes of PCOD and PCOS?
Causes of PCOS
The exact reason for PCOS is not fully understood, but it is believed to be a complex interplay of genetic and environmental factors. Some potential causes include:
- Insulin Resistance: Insulin resistance is a key factor in PCOS, resulting in elevated insulin levels and increased androgen production.
- Hormonal Imbalances: Imbalances in hormones like androgens, oestrogen, and progesterone can contribute to the development of PCOS.
- Genetics: Polycystic ovary syndrome tends to run in families, implying a genetic component.
- Obesity: Being overweight or obese can exacerbate insulin resistance and hormonal imbalances, increasing the risk of PCOS.
Causes of PCOD
The causes of PCOD are not as well-defined as those of PCOS. However, some potential contributing factors include:
- Hormonal Changes: Fluctuations in hormones during puberty or menopause may lead to the development of PCOD.
- Genetics: Like PCOS, PCOD may have a genetic component.
- Lifestyle Factors: Factors such as diet, stress, stretches, and exercise levels may play a role in developing PCOD.
Also read: The Impact of Stress on Men’s and Women’s Sexual Health
Which is more Complicated – PCOD or PCOS?
PCOS is generally considered a more complex and multifaceted condition compared to PCOD. PCOS involves a range of hormonal imbalances, metabolic disturbances, and potential long-term health risks, making it a more complicated condition to manage and treat. On the other hand, PCOD is often considered a milder form of the condition and may not necessarily require extensive treatment or management.
PCOS/PCOD Problem in Future
Both PCOS and PCOD can have long-term implications for a woman’s health and well-being if left unmanaged. Women with PCOS are at an increased likelihood of developing metabolic disorders, like type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, and endometrial cancer. Additionally, PCOS is a leading cause of infertility, which can have substantial emotional and psychological effects.
Women with PCOD may also experience fertility issues and an increased possibility of certain health complications, although typically to a lesser degree than those with PCOS. Regular monitoring and appropriate management approaches are essential for both conditions to prevent potential future health problems.
Can Women Get Pregnant When She has PCOD?
Women with PCOD can get pregnant, although their chances of conceiving may be slightly lower compared to women without the condition. PCOD is generally considered a milder form of PCOS, and many women with PCOD do not experience significant fertility issues.
However, it is essential to note that each woman’s experience with PCOD can vary, and some may face challenges with ovulation and conception. In such cases, seeking medical advice and exploring appropriate treatment options, such as ovulation-inducing medications or assisted reproductive technologies, may be necessary.
How can I Reduce PCOD/PCOS Naturally?
While medical interventions may be necessary in some cases, several natural approaches can help manage the symptoms and reduce the impact of PCOD and PCOS:
Dietary Changes
A balanced, nutrient-rich diet can help regulate hormones, promote weight management, and improve insulin sensitivity. Focus on consuming whole, unprocessed foods, including fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Limit your consumption of sugary foods, refined carbohydrates, and unhealthy fats.
Probiotics
Probiotics, or beneficial gut bacteria, have been shown to improve insulin sensitivity and diminish inflammation, both of which are crucial factors in PCOS and PCOD. Add probiotic-rich foods like yoghurt, kefir, and fermented vegetables to your meals, or take a high-quality probiotic supplement.
Weight Management:
Maintaining a healthy weight or shedding extra weight can improve insulin sensitivity, regulate hormones, and alleviate PCOS and PCOD symptoms. Combine a well-balanced meal with regular exercise to achieve and maintain a healthy body weight.
Exercises
Regular workout not only aids in weight management but also help improve insulin sensitivity, reduce inflammation, and promote overall well-being. Engage in a combination of cardio training and strength training exercises.
Stress Reduction
Chronic stress can exacerbate hormonal imbalances and worsen PCOS and PCOD symptoms. Incorporate stress-reducing techniques like mindfulness, deep breathing exercises, or meditation into your daily routine.
Herbal Supplements
Certain herbal supplements, such as inositol, cinnamon, and spearmint, have been shown to have potential benefits for managing PCOS and PCOD symptoms. However, consulting a doctor before incorporating supplements into your regimen is essential.
Avoiding Endocrine Disruptors
Endocrine disruptors are chemicals found in various products that can interfere with hormonal balance. Limit your exposure to endocrine disruptors by avoiding plastics, certain personal care products, and pesticides whenever possible.
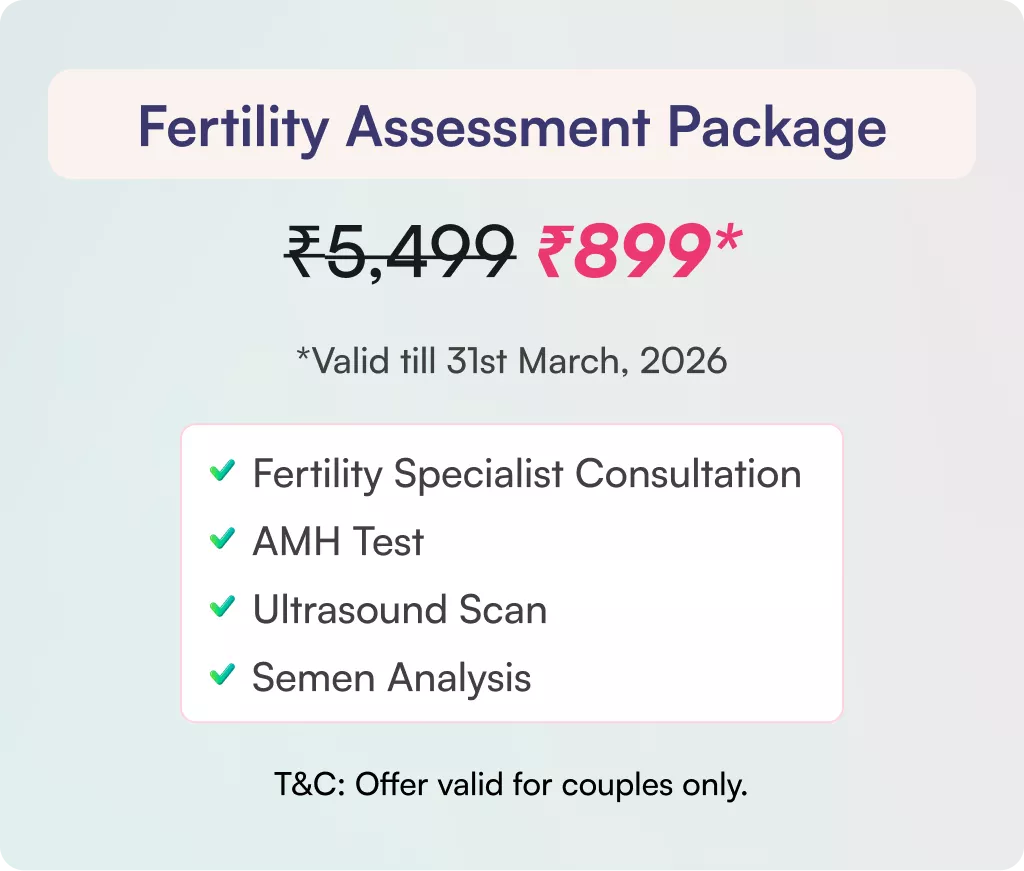
Find Hope and Solutions for Female Infertility — Explore Our Comprehensive Services
IVF Treatment
IUI Treatment
ICSI Treatment
PICSI Treatment
Fertility Preservation Service
Blastocyst Culture & Transfer Treatment
Genetic Screening & Testing
Conclusion
While PCOD and PCOS share some resemblances, they are distinct conditions with varying degrees of complexity and potential health implications. Understanding the differences between PCOD and PCOS is crucial for proper diagnosis, treatment, and management.
PCOS is a more complex condition involving hormonal imbalances, ovulatory dysfunction, and metabolic disturbances, while PCOD is often considered a milder form characterised by the presence of ovarian cysts. Proper medical evaluation, lifestyle modifications, and appropriate treatment strategies are essential for managing both conditions and preventing potential long-term health risks.
By accepting a holistic approach that combines dietary changes, regular exercise, stress management, and appropriate medical interventions when necessary, women with PCOD or PCOS can effectively manage their symptoms and boost their overall health.

























 No need to worry, your data is 100% safe with us!
No need to worry, your data is 100% safe with us!