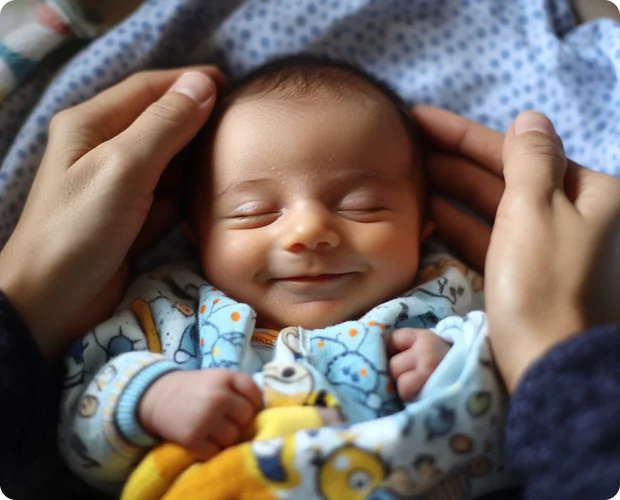
Many women consider using menstrual pills to adjust their period dates for important events or travel plans. While these medications offer convenience in managing menstrual timing, questions often arise about their effects on reproductive health. Period delay tablet side effects can range from mild to significant, particularly when these medications are used frequently or incorrectly. Understanding how these pills affect fertility and overall reproductive health is crucial for females who are planning for pregnancy or are concerned about their future fertility.
Struggling to conceive? Check our IVF Treatment Cost and Success Rates to plan your journey.
Learn more about the Period Calculator in our detailed guide.
How Menstrual Pills Work?
Menstrual pills function through a precise combination of hormones that regulate the reproductive system. These medications primarily contain two key hormones: progestin and oestrogen. The combination of these hormones works systematically to control the menstrual cycle and prevent pregnancy.
The pills operate through several vital mechanisms:
- Preventing ovulation by inhibiting follicular development
- Thickening cervical mucus to form a barrier against sperm
- Thinning the uterus lining to prevent implantation
- Regulating hormone levels throughout the menstrual cycle
Two main types of menstrual pills exist- the combination pill and the minipill. The combination pill contains both progestin and oestrogen, typically coming in packs with 21-24 active hormone pills and 4-7 inactive pills. This arrangement helps regulate the menstrual cycle by allowing scheduled bleeding during inactive pill days. The minipill, containing only progestin, comes in packs of 28 active pills with no inactive pills.
These medications work by creating a controlled hormonal environment. When taken consistently, they affect the hypothalamus and pituitary gland, reducing the secretion of follicle-stimulating hormone and luteinising hormone. This hormonal regulation prevents the development of follicles and stops the mid-cycle surge that typically triggers ovulation.
The effectiveness of menstrual pills depends on consistent daily intake. It typically takes up to seven days for the pills to establish their full protective effect, during which time additional contraceptive measures may be necessary.
Preponing Menstrual Cycle: How It Affects Fertility
Changes in menstrual cycle timing can significantly impact reproductive health. When women use medications to prepone their periods, it affects the natural hormonal balance that regulates fertility. The body’s reproductive system operates on a delicate schedule, with the typical menstrual cycle lasting between 23 to 35 days.
Preponing periods through medication can disrupt the natural follicular phase, which is crucial for proper egg development. This disruption may lead to several effects on fertility:
- Irregular ovulation patterns
- Changes in cervical mucus quality
- Altered endometrial development
- Unpredictable cycle lengths
- Hormonal imbalances affecting egg maturation
The impact of early periods on fertility largely depends on how frequently the cycle is altered. Short-term changes typically don’t cause lasting effects, but regular manipulation of the menstrual cycle can lead to irregular periods. Women who frequently adjust their cycle timing may experience variations in their follicular phase, which is the primary determinant of cycle length variability.
Medical research indicates that most women’s luteal phase remains relatively constant at around 14 days. However, when periods are preponed, the natural hormone production sequence may be disrupted, potentially affecting the timing of ovulation. This disruption can make it more challenging to predict fertile days and may temporarily impact conception chances.
Postponing Menstrual Cycle: Effects on Fertility
Postponing menstrual cycles through hormonal medications has become increasingly common for women seeking to manage their periods around significant life events. Several methods exist to postpone the period, each with distinct effects on reproductive health.
Combined hormonal contraceptives offer a reliable way to delay periods safely. When used correctly, these medications do not cause permanent fertility changes. The effects are temporary; regular cycles typically resume within 3 to 6 months after discontinuation.
Different methods for postponing periods include:
- Combined oral contraceptive pills with continuous use
- Hormonal IUDs (varying doses available)
- Injectable contraceptives (effective for 90 days)
- Period delay tablets containing norethisterone
Research indicates that 50% to 75% of women using injectable contraceptives experience an absence of periods after one year of use. However, fertility returns gradually after discontinuation. The time frame for fertility restoration varies depending on the method used, with most women regaining their natural cycle within six months.
It’s important to note that period-delay tablets are not contraceptives and should not be used for pregnancy prevention. Women using progesterone-only contraceptive methods should consult their doctor before using additional period delay medications, as combining these treatments requires medical supervision.
For women concerned about future fertility, current evidence shows that modern low-dose hormonal methods do not cause long-term fertility problems. Any temporary delays in conception after stopping these medications are typically brief and resolve naturally as the body returns to its regular hormonal patterns.
Can Preponing or Postponing Pills Cause Infertility?
Recent scientific research has conclusively demonstrated that menstrual pills do not cause permanent infertility. This finding addresses one of the most common concerns among women who use period-delay tablets or other hormonal contraceptives.
Studies show that fertility returns to normal levels after discontinuing menstrual pills, with most women regaining their natural reproductive capacity within 3-6 months. The duration of contraceptive use has no significant impact on future fertility, whether used for a few months or several years.
Research data reveals encouraging statistics about fertility restoration:
- 65-85% of women successfully conceive within one year of stopping contraceptives
- Fertility returns faster with non-hormonal methods compared to hormonal ones
- Most women experience regular ovulation within 2-5 months of discontinuation
- The median time to pregnancy is slightly longer for injectable contraceptives at 7-8 months
It’s important to note that some women may experience temporary irregularities when stopping menstrual pills. These changes are typically short-term adjustments as the body returns to its natural hormone production. Sometimes, what appears to be pill-related infertility may actually be pre-existing conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome that were masked by the regular cycles created by contraceptives.
Medical evidence confirms that modern low-dose contraceptive regimens are safe for long-term use. Any delays in conception after discontinuation are temporary, and more than 82% of women achieve pregnancy within 24 months of stopping contraceptive use.
When to Consult a Doctor
Doctors emphasise the importance of professional medical supervision when using period delay tablets or other menstrual cycle medications. Regular monitoring helps prevent the side effects of period delay tablets and ensures optimal reproductive health.
Women should seek immediate medical attention if they experience:
- Severe abdominal pain or cramping
- Unusually heavy bleeding (soaking through protection hourly)
- Foul-smelling vaginal discharge
- Periods lasting longer than seven days
- Irregular bleeding between cycles
- Persistent nausea or vomiting
- Sudden changes in cycle duration
- Missing periods for three or more months
Regular health monitoring is essential while using hormonal medications. Women should schedule routine pelvic examinations, Pap tests, and blood pressure checks. Those using specific medications like depot medroxyprogesterone require bone density monitoring to prevent potential bone loss.
Before starting any menstrual regulation medications, discussing medical history with doctors is essential. This allows for informed decisions based on individual health factors and reproductive goals. Women should track their symptoms and promptly report any persistent side effects to their doctor.
Safe Use of Menstrual Pills
The safe and effective use of menstrual pills requires careful attention to proper administration and timing. Doctors recommend following specific guidelines to minimise risks and optimise these medications’ benefits.
For optimal effectiveness and safety, women should:
- Take pills at the same time each day
- Start the medication between days 3-5 of menstruation
- Maintain consistent daily intake
- Use additional protection during the first week
- Report unusual symptoms promptly
- Store medications at room temperature
- Check interactions with other medications
Effectiveness rates vary based on usage patterns. When taken correctly, menstrual pills demonstrate a 93% success rate in regulating cycles and preventing pregnancy. However, missing doses or incorrect timing can significantly reduce their reliability.
Women experiencing period delay pill side effects like nausea, headaches, or breast tenderness should know these typically resolve within 2-3 months. If symptoms persist beyond this period, consulting a doctor is essential. For those who experience vomiting within two hours of taking the pill, repeating the dose is necessary to maintain effectiveness.
Special considerations apply to specific groups. Breastfeeding mothers should opt for progestin-only pills, as combination pills might affect milk production. Women with underlying health conditions need individualised guidance from their doctors to ensure safe usage.
Regular monitoring helps identify potential issues early. Doctors recommend scheduling check-ups every 6-12 months to assess overall health and adjust medications if needed. This proactive approach helps maintain reproductive health while safely managing menstrual cycles.
Find Hope and Solutions for Female Infertility and Male Infertility — Explore Our Comprehensive Services
IVF Treatment
IUI Treatment
ICSI Treatment
PICSI Treatment
Fertility Preservation Service
Blastocyst Culture & Transfer Treatment
Genetic Screening & Testing
Conclusion
Menstrual pills offer women flexibility in managing their periods without causing permanent fertility problems. Research shows that both preponing and postponing periods through hormonal medications have temporary effects that resolve within 3-6 months after stopping the pills. Most women return to their natural cycles and achieve pregnancy within a year of discontinuation.
The safety of these medications depends mainly on proper usage and regular medical supervision. Women should track their symptoms, maintain consistent dosing schedules, and promptly report any unusual side effects to their doctors. This careful approach helps prevent complications and ensures optimal reproductive health.
Medical evidence supports the use of modern low-dose hormonal medications for menstrual regulation when needed. Women considering these options should discuss their reproductive goals and medical history with doctors to create a safe and effective treatment plan.