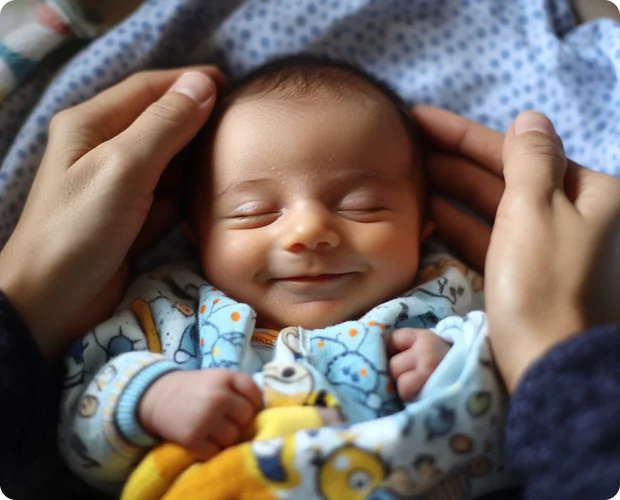
More women today are choosing to delay starting a family, making late-age pregnancy an increasingly common choice. Medical advances have made it possible for women to become mothers well into their 30s and 40s, though this decision comes with its own set of considerations.
While advanced maternal-age pregnancy requires careful planning and monitoring, many women successfully navigate this journey with proper medical support. Understanding the risks and challenges of getting pregnant later in life is crucial, as is knowing how to maintain optimal health throughout the process. This comprehensive guide explores everything expectant mothers need to know about advance age pregnancy, from potential health considerations to essential lifestyle adjustments that can help ensure a healthy pregnancy journey.
Also read: Pros And Cons Of Getting Pregnant In Your 20s, 30s, And 40s!
What Is Considered Late-age Pregnancy?
The medical community defines advanced maternal age as pregnancy at 35 years or older at the time of delivery. While doctors previously used the term “geriatric pregnancy,” this outdated phrase has been replaced with more respectful terminology. Current global trends show more people choosing to delay parenthood.
Understanding late-age pregnancy requires recognising that age-related changes occur gradually. Fertility begins to decline around age 30, with a more noticeable decrease during the mid-30s. By age 45, conceiving naturally becomes significantly less likely due to reduced egg quality and quantity.
Doctors now recognise that age-related pregnancy considerations exist on a continuum rather than suddenly appearing at age 35. This understanding has led to a more nuanced approach to pregnancy care, with doctors typically categorising advanced maternal age into different groups: 35 to 39 years, 40 to 44 years, 45 to 49 years, and 50 years & older.
It’s important to note that while age 35 serves as a medical benchmark, this threshold was originally established based on older genetic testing criteria. Modern medical advances have improved pregnancy outcomes for those choosing late-age pregnancy, and many healthy individuals who conceive after 35 successfully deliver healthy babies. However, doctors recommend additional monitoring and screening for pregnancies in this age group to ensure optimal outcomes.
Also read: Does age affect fertility treatment?
Risks of Pregnancy Over Age 30
Pregnancy after age 30 brings specific health considerations that require careful monitoring and management. While many women have healthy pregnancies in their 30s and beyond, understanding potential risks helps make informed prenatal care decisions.
Chromosome Problems
The risk of chromosomal abnormalities increases significantly with maternal age. By age 40, the chance of having a child with Down syndrome rises to about 1 in 100, compared to 1 in 1,250 for women who conceive at age 25. This increase occurs because older eggs are more likely to have irregular chromosome division during development.
Also read: The Role of Genetics in Recurrent Implantation Failures
Miscarriage
The likelihood of pregnancy loss shows a clear correlation with age. Women between 30-34 face a 12% risk of miscarriage, while those between 35-37 see this increase to 16%. The risk continues to rise, reaching approximately 33% for women aged 40-41. This elevated risk primarily stems from the higher occurrence of chromosomal abnormalities in eggs as women age.
Twins
Multiple pregnancies become more common in women over 35. This increased likelihood stems from higher levels of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH). Higher levels of folic acid can cause the release of multiple eggs during ovulation. Women undergoing fertility treatments also face higher chances of multiple pregnancies due to the nature of these treatments.
Gestational Diabetes
Gestational diabetes poses a particular concern for older mothers. This condition can affect how cells use sugar and may lead to:
- Increased likelihood of requiring a caesarean section
- Higher risk of early labour and delivery
- Possible respiratory difficulties for the baby
High Blood Pressure
Pregnancy-related hypertension becomes more common with advancing maternal age. High blood pressure during pregnancy can develop in two forms: chronic hypertension (present before 20 weeks) or gestational hypertension (developing after 20 weeks). Both types require careful monitoring as they can lead to complications such as:
- Preeclampsia
- Restricted foetal growth
- Increased risk of preterm delivery
These risks shouldn’t discourage women from pursuing pregnancy after 30 but rather emphasise the importance of proper prenatal care and regular medical monitoring. Many women successfully navigate these challenges with appropriate medical support and lifestyle modifications.
How to Make Healthy Choices
Making healthy choices becomes crucial for women pursuing late-age pregnancy. Doctors recommend several key strategies to optimise both maternal and foetal health during this important journey.
Fertility Preservation
Women considering pregnancy after 35 should discuss fertility preservation options with their doctors early. Fertility preservation protects reproductive tissues for future pregnancy possibilities. The optimal timing for preservation is by age 35 for women who have no immediate plans for children. Various methods exist, including egg freezing and embryo cryopreservation, which offer the highest success rates.
Eat a Healthy Diet
Proper nutrition plays an elementary role in supporting a healthy pregnancy at an advanced age. A balanced diet should include essential nutrients supporting maternal and foetal health. Doctors recommend:
- Whole grains, fruits & vegetables for fibre and vitamins
- Lean proteins and low-fat dairy products
- Foods rich in folate, iron, and calcium
- Adequate water intake for proper hydration
- Limited processed foods and sugary drinks
Maintain Healthy Lifestyle
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle becomes especially important for women experiencing pregnancy at an advanced age. When approved by doctors, regular physical activity can help manage weight gain & reduce the complication risk. Essential lifestyle modifications include:
- Moderate exercise appropriate for pregnancy
- Adequate sleep and stress management
- Regular prenatal checkups
- Avoiding alcohol, smoking, and caffeine
- Managing any existing health conditions
Prenatal Testing for Chromosomal Conditions
Women pursuing late-age pregnancy should understand their prenatal testing options. Modern screening methods can provide valuable information about potential chromosomal conditions. The quad marker screen can detect approximately 75-80% of neural tube defects and various genetic disorders. Additional investigations include amniocentesis and chorionic villus sampling (CVS), which provide more detailed genetic information when needed.
Advanced Fertility Treatments for Late-age Pregnancy
Recent advances in reproductive medicine have opened new possibilities for women pursuing pregnancy at an advanced age. Assisted reproductive technologies (ARTs) have become increasingly sophisticated, offering multiple pathways to parenthood for those experiencing age-related fertility challenges.
In Vitro Fertilisation (IVF): IVF remains the most effective treatment for late-age pregnancy. The process involves several key steps:
- Ovarian stimulation through hormone medications
- Egg retrieval under medical supervision
- Laboratory fertilisation of eggs with sperm
- Embryo development monitoring
- Transfer of selected embryos to the uterus
Success rates for IVF vary significantly with age. Women should be aware of the following statistics:
- Age 30-34: approximately 25% live birth rate per cycle
- Age 35-37: about 20% success rate
- Age 38-40: roughly 15% success rate
- Age 41-42: approximately 7% success rate
Egg Donation: This process has emerged as a valuable option for women over 40. Research shows that the uterine environment of older women can successfully support pregnancy when using donor eggs from younger women. This approach has demonstrated success rates comparable to those of younger women undergoing IVF with their own eggs.
Fertility Preservation: For women considering future pregnancy, fertility preservation through egg freezing offers a proactive solution. The optimal time for egg freezing is before age 35 when egg quality and quantity are typically higher. This process involves harvesting and freezing eggs for future use, essentially pausing the biological clock.
Medical screening plays a crucial role in determining the most appropriate treatment path. Doctors conduct comprehensive evaluations to assess overall health, reproductive potential, and any age-related risks. This personalised approach helps identify the most suitable fertility treatment options for each individual.
Conclusion
Late-age pregnancy presents both unique challenges and opportunities for women choosing to start families after 35. Medical advances have made successful pregnancies possible for many women in their late 30s and early 40s, though careful planning remains essential.
Doctors now offer comprehensive support systems, from advanced prenatal testing to specialised fertility treatments. The decision to delay pregnancy requires careful consideration of personal health, available medical support, and potential risks. Women pursuing pregnancy at an advanced age can maximise their chances of success through proper nutrition, regular exercise, and early discussions about fertility preservation options.