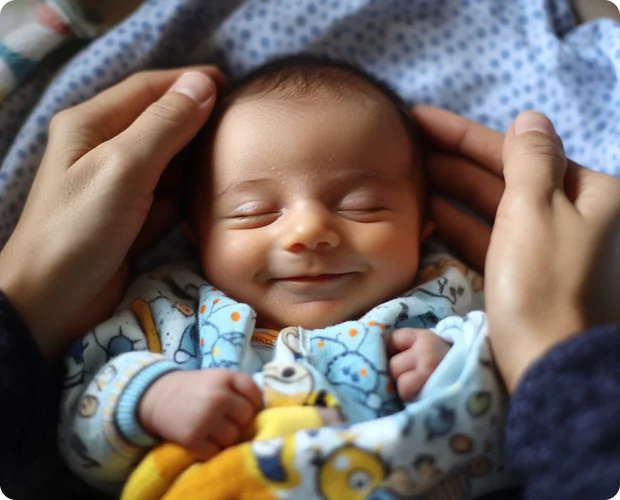
Infertility in India is becoming a major public health concern. The nation, which was formerly renowned for having high fertility rates, has experienced a dramatic drop in birth rates in recent decades, coupled with an increase in cases of infertility. Urbanization, modified lifestyles, delayed marriages, shifting career priorities, and rising contraceptive usage are some of the causes of infertility. However, for a variety of reasons, infertility rates have also been on the rise.
Also read: Did You Know 1 in 6 People Globally Are Affected by Infertility?
Current Infertility Rates in India
An estimated 10-15% of couples in India are having trouble conceiving, and the country’s infertility rates have been continuously growing. This corresponds to around 27.5 million infertile couples nationwide. Infertility cases in India also differ according to the duration of marriage. Infertility, for instance, was more common in women who had been married for one year in 2019–2020 (42.9/1,000) than in those who had been married for four years (20.7/1,000).
Causes of Infertility in India
In India, infertility rates are high due to lifestyle variables, and the causes of infertility include stress, poor diet, pollution, and postponed childbirth. Both men and women experience infertility, and the prevalence is significantly higher in urban areas. Male infertility is mostly caused by deteriorating sperm quality, whereas infertility in women is largely caused by health issues like obesity, endometriosis, and Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS). Additionally, many couples are at a higher risk of experiencing reproductive issues as a result of delayed marriages and late pregnancies.
Increasing Infertility Rates
Significant relationships are found between infertility and lifestyle factors, age of marriage, and biological traits. Failure to conceive after a year or more of trying without prior successful pregnancies is known as primary infertility. A higher level of education and late marriage are linked with a higher incidence of primary infertility. When people who have once conceived are unable to conceive again, it’s known as secondary infertility. This might happen because of age, changes in lifestyle or health issues (non-communicable diseases) that emerged after their first pregnancy. Between 1992 and 2015, primary infertility significantly decreased, whereas secondary infertility rose from 19.5% in 1992–1993 to 28.6% in 2015–16. This pattern is associated with decreasing fertility rates, especially in the southern regions of India.
Age-Related Factors
An important contributing element to India’s growing infertility rates is age-related variables. Aging in both men and women can lead to increasing health difficulties such as hormone imbalances and genetic disorders, limiting fertility efforts. Beyond the age of 30, women’s fertility starts to diminish, and it does so more quickly beyond the age of 35. This increases the risk of infertility, pregnancy difficulties, and miscarriage. Men’s fertility falls with age, with lower sperm quality and count usually beginning around the age of 40.
Hormonal imbalances, ovulation problems, anatomical problems with the reproductive organs, age-related reduction in fertility, and medical illnesses like endometriosis or polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) are some of the causes of female infertility crisis.
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is the main cause of infertility in women, affecting over 10% of women of reproductive age worldwide, including India. Fertility rates are severely impacted by Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS). Because of their inconsistent or absence of ovulation, women with PCOS have trouble becoming pregnant naturally. Furthermore, PCOS is associated with other disorders, such as obesity, which can further affect fertility health.
Endometriosis
Up to 30–50% of women who have trouble becoming pregnant are affected by endometriosis, which is a prevalent cause of infertility. In endometriosis, tissues that resemble the lining of the uterus develop outside of it, resulting in discomfort and inflammation. The ovaries and fallopian tubes may become distorted as a result of these abnormalities, making it more difficult for the egg to be released or fertilized.
Male Infertility Factors
The rise in male infertility that has been happening globally since the 1970s is known as the “male infertility crisis.” Low sperm count, poor sperm motility, and aberrant sperm morphology are some of the reasons that contribute to male infertility, a condition where a man faces challenges in helping his female partner conceive. Medical disorders, including diabetes or infections, as well as hormonal abnormalities, can potentially affect fertility. Lifestyle behaviors that have a detrimental impact on sperm health include smoking, alcohol consumption, and obesity.
Lifestyle Choices
In both men and women, unhealthy lifestyle choices, including smoking, alcohol, and drug usage, can have a negative impact on well-being and affect fertility health. Hormonal imbalances and metabolic problems that affect ovulation and sperm production might result from poor eating habits, inactivity, and obesity. High stress and sleep deprivation can also have a detrimental effect on hormone control, which exacerbates infertility rates.
Lack of Awareness and Education
A major problem is still the lack of understanding and awareness of infertility, particularly in developing nations like India, which leads to the human fertility crisis. Many people are ignorant of the lifestyle, age, and health issues that affect fertility, which leads to delayed diagnosis and treatment. Couples are unaware of the available treatment alternatives, such as assisted reproductive technologies (ART), because of the social stigma associated with infertility, which further prevents open conversations. Furthermore, emotional and psychological suffering is made worse by misconceptions about reproductive health. In these circumstances, it is crucial to implement education and awareness-raising initiatives to address knowledge of the prevalence and contributing factors of infertility and fertility.
Environmental Factors
Numerous environmental variables can affect infertility rates, which in turn affect human reproduction and health. Urbanization, radiation exposure, pollution, and climate change affect fertility and have a greater impact on male and female fertility issues.
Access to Fertility Treatments in India
Although there are still obstacles, access to reproductive therapies in India has been gradually getting better. Advanced fertility clinics offering Assisted Reproductive Technologies (ART), including Intrauterine Insemination (IUI) and In Vitro Fertilization (IVF), are increasing in major metropolitan centers, making these procedures more accessible to infertile couples.
Current Government Initiatives at Improving Reproductive Health
With an emphasis on family planning, maternal health, and adolescent reproductive education, the Indian government has put in place a number of initiatives to enhance reproductive health. Important projects include:
- Pradhan Mantri Surakshit Matritva Abhiyan (PMSMA)
- Janani Suraksha Yojana (JSY)
- National Health Mission (NHM): Reproductive, Maternal, Newborn, Child, and Adolescent Health (RMNCH+A)
- Mission Parivar Vikas
Preventive Measures to Reduce Infertility Rates?
Numerous factors can contribute to infertility, but both men and women can lower their chance of experiencing it by taking preventive actions such as
- Healthy lifestyle
- Reduce stress
- Avoid smoking and alcohol
- Limit exposure to harmful environmental toxins
- Regular medical checkups
- Awareness and education about reproductive health and fertility
- Safe sexual practices
People can reduce their risk of infertility and improve their general reproductive health by following these preventative strategies.
Find Hope and Solutions for Female Infertility and Male Infertility — Explore Our Comprehensive Services
IVF Treatment
IUI Treatment
ICSI Treatment
PICSI Treatment
Fertility Preservation Service
Blastocyst Culture & Transfer Treatment
Genetic Screening & Testing
Conclusion
Infertility cases are on the rise in India, mostly due to environmental factors, delayed pregnancy, and changes in lifestyle. Despite the availability of fertility treatments, access to them varies across urban and rural communities. To solve this issue, government initiatives and awareness-raising activities are essential. In developing countries like India, the issue of infertility might be alleviated by early detection and treatment.