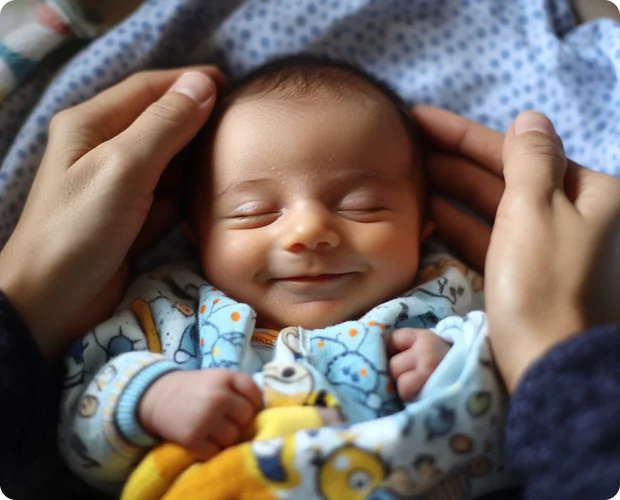
With millions of individuals and couples trying to conceive, assisted reproductive technology (ART) has had a significant impact on infertility. This technology increases the number of reproductive options available to those who would not have otherwise had the chance to have a family. With the help of ART, fertility treatment has changed, enabling millions of people to build families and realize their dream of becoming parents. The assisted reproductive technologies (ART) laws in India guarantee individuals and couples safe, ethical, and successful fertility treatments.
What is Assisted Reproductive Technology and It’s Importance
Infertility is the most common reason for using assisted reproductive technology. The treatment for infertility involves the use of assisted reproductive technology (ART). It covers reproductive procedures that deal with both sperm and eggs. These sperm and eggs are fused to form embryos. Following that, the embryos are placed back into the mother’s uterus.
In vitro fertilization (IVF), intrauterine insemination (IUI), egg retrieval, embryo freezing, and intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) are the fundamental ART procedures. The most popular and successful ART is in vitro fertilization (IVF). When a patient has tubal factor infertility, IVF bypasses the fallopian tubes directly. IVF is also used to treat male factor infertility, premature ovarian insufficiency (using donor eggs), ovulatory dysfunction, reduced ovarian reserve, and unexplained infertility.
Typically, the minimum age for ART IVF is 21, and the maximum age for IVF is 50 in women. Whereas in men it is 21 and 55. In the case of IUI, the age limit for women is at least 21 years old and no older than 35 to 40.
One major advantage of ART in vitro fertilization (IVF) is that it can help infertile individuals and couples become pregnant and have biological children, even in difficult reproductive circumstances. However, in a few cases, in vitro fertilization (IVF) carries risks to the mother, including ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS), which can cause ovarian swelling and fluid retention. Although there are certain hazards associated with IVF, these are frequently outweighed by the fact that it offers people and couples who are having trouble becoming pregnant.
Key Objectives of these New ART Regulations
The following are the main goals of India’s new Assisted Reproductive Technology (ART) Regulations:
Ensuring Ethical Practices:
To avoid the exploitation of patients, donors, and children born via ART methods, as well as to encourage transparency and moral behavior in reproductive treatments.
Regulating ART Fertility Clinics and Banks:
To assure the safety and quality of ART services, all ART fertility clinics and banks must be duly registered under the National Assisted Reproductive Technology and Surrogacy Registry and adhere to strict medical needs.
Eligibility Requirements for Donors and Commissioning Parties:
Married couples or (i) women who are between the ages of 21 and 50 and (ii) men between the ages of 21 and 55 may request ART treatments. A bank can get eggs from females between the ages of 23 and 35 and semen from males between the ages of 21 and 55. A maximum of seven eggs may be extracted from the donor, and the woman may only contribute eggs once in her lifetime.
Preserving the Rights of All Parties:
To protect the rights and well-being of intended parents, donors, and ART-born children while guaranteeing informed consent and privacy throughout the whole process.
Preventing Technology Misuse:
To preserve the integrity of ART technology by preventing unethical practices such as sex selection, embryo commercialization, or unapproved activities.
How have ART Laws Changed the Landscape of Fertility Care?
By creating a regulated framework for ART fertility clinics and banks, the new ART rules in India have drastically changed the reproductive care industry and ensured safer and more moral procedures. By enforcing appropriate registration and monitoring of ART treatments, they have increased transparency and raised the standard of care. By prohibiting exploitation and negligence, the rules also safeguard the health and rights of patients, donors, and ART-born children. In general, they have improved the reliability, ethics, and accessibility of fertility care for people in need of reproductive support.
How Regulations Impact Increased Fertility Treatment Costs?
As ART fertility clinics and banks must now adhere to more stringent ART regulations, the cost of reproductive treatments has increased in India. ART facility accreditation, registration, and routine inspections increase operating costs, which are eventually transferred to patients. Clinics have to spend more money on better equipment, infrastructure, and trained personnel in order to satisfy greater requirements, which raises expenses even more. Laws requiring accurate documentation, tracking, and reporting can increase administrative costs. Although safety and transparency are improved by these restrictions, the overall cost of reproductive treatments has also increased.
Increased Costs Creating Limitations on Conception Opportunities
For many individuals and couples seeking support with conception, the rising costs of reproductive treatments due to stricter guidelines present financial obstacles. Access to treatments like IVF is hampered by higher costs, particularly for low and middle-income couples. People who can’t afford the growing costs have fewer possibilities, which lowers their chances of becoming parents. The financial strain of treatment expenses can also lead to inequalities in access to reproductive care.
Potential Long-Term Effects of New ART Laws
Better protection for patients, donors, and ART-born children is anticipated as a result of India’s new ART regulations, which are expected to improve the safety, openness, and moral standards of reproductive treatments. They could eventually lessen industrial exploitation and misconduct, increasing public confidence in reproductive technology. Over time, these rules may lead to a fertile landscape that is more controlled yet less accessible.
Conclusion
An important step toward guaranteeing moral, secure, and transparent fertility treatments has been taken with India’s new ART regulations. The regulations seek to avoid exploitation and enhance the quality of care by regulating clinics and safeguarding the rights of donors and recipients. Accessibility and high standards still need to be balanced, even if these rules promote responsibility and confidence in the fertility sector. In the end, the regulations offer a solid foundation for a more moral and well-regulated reproductive care system in India.