Role of Genetics in Male Infertility
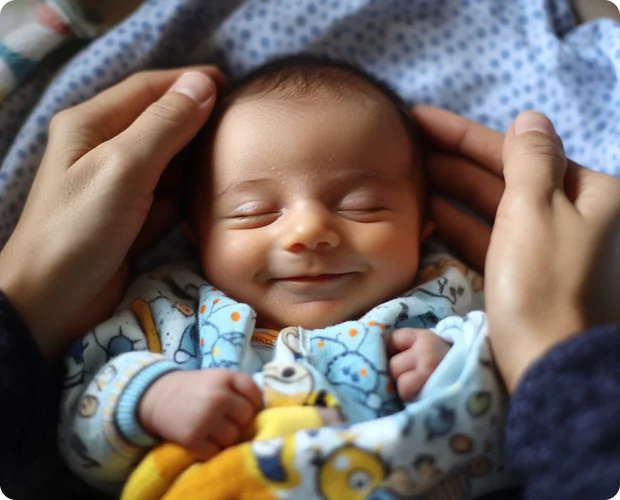
Infertility can be emotionally and physically draining, and male factors play a crucial role as well. The DNA Fragmentation Index (DFI) is a useful tool for assessing male fertility by examining sperm DNA integrity, which provides more information than standard semen analysis.
Sperm carry the genetic blueprint to the egg. Although they may look healthy under a microscope, their DNA can be damaged or fragmented. Sperm DNA fragmentation can greatly affect a couple’s chances of conceiving. It can also impact the health of the pregnancy.
What is the role of DFI in Male infertility?
Here’s why DFI is so important in the context of male infertility:
- Impaired Fertilization: A sperm with fragmented DNA can fertilize an egg. But the damaged genes may stop the embryo from developing properly.
- Reduced Embryo Quality: Higher sperm DNA fragmentation leads to lower embryo quality. This affects implantation rates and raises the risk of early pregnancy loss.
- Increased Miscarriage Risk: Studies show that higher DFI raises the risk of miscarriage. This applies to both natural conception and assisted reproductive technologies (ART).
- High DFI can reduce fertilization rates in IUI and IVF. It can hinder embryo development, lower implantation success, and harm overall pregnancy outcomes.
- Childhood Disease Link: Some studies suggest that high sperm DNA fragmentation may raise the risk of health problems in children.
DFI offers key insights beyond regular semen analysis. It reveals hidden factors that might cause infertility.
What Causes DNA Fragmentation?
It’s important to know what can raise DFI. This helps in choosing the right management strategies. Several factors can contribute to sperm DNA damage, including:
- Oxidative Stress: If free radicals are too high and antioxidants are too low, sperm DNA can be damaged.
- Infections and inflammation: Infections in the male reproductive tract can increase oxidative stress and trigger inflammation. This can lead to DNA fragmentation.
- Varicocele: Enlarged veins in the scrotum can raise testicular temperature and reduce oxygen. This may harm sperm DNA.
- Environmental Toxins: Some pollutants, pesticides, and heavy metals can raise DFI levels.
- Lifestyle Factors: Smoking, drinking too much alcohol, being obese, and having a bad diet can harm sperm DNA.
- Advanced Paternal Age: Sperm DNA fragmentation often increases as the male partner gets older.
- Testicular Hyperthermia: When the testicles get too hot from tight clothing, sitting too long, or fever, it can damage sperm DNA.
Techniques to assess the extent of sperm DNA fragmentation
Every technique exhibits its strengths and weaknesses. Sensitivity, specificity, cost, and implementation ease are key factors. Choosing the right method hinges on the lab’s expertise and its resources.
- Sperm Chromatin Structure Assay (SCSA) uses flow cytometry to assess how sperm DNA can break down in acidic conditions.
- DFI and High DNA Stainability (HDS) are important. They show the percentage of sperm with fragmented DNA and the amount of immature sperm.
- The TUNEL assay identifies DNA strand breaks. It labels the ends of fragmented DNA.
- Single Cell Gel Electrophoresis, known as the Comet Assay, tests for DNA damage in single sperm.
Decoding the Numbers: Understanding DFI Cutoff Ranges
Interpreting DFI results is crucial for clinical decision-making. Cutoff values can differ between labs and methods. However, here are the commonly accepted ranges and their meanings:
- DFI < 15% (or 20% depending on the assay): This level usually means good sperm DNA integrity. It also suggests a high chance of natural conception and successful ART outcomes.
- DFI of 15-25% (or 20-30%) shows moderate DNA fragmentation. This can hurt fertility potential. Natural conception is possible, but the chances are not great. This could also lower ART success rates.
- DFI over 25% (or 30%) means high DNA fragmentation. This lowers the chances of natural conception. It also reduces success rates with ART. This level of fragmentation is often associated with an increased risk of miscarriage.
These cutoff ranges are meant as guidelines. It’s crucial to consider each patient’s history, other semen factors, and the specific ART procedure being used.
Sperm Sorting Techniques
- Magnetic-Activated Cell Sorting (MACS) uses magnetic microbeads to spot and remove damaged sperm. This method can raise pregnancy rates by 10-15% for patients with high DFI.
- Microfluidics: It uses devices designed like the female reproductive tract. These devices choose motile sperm that have better morphology and lower DNA fragmentation.
- Physiological Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection (PICSI) picks sperm that can bind to hyaluronan. This substance is in the egg’s outer layer.
- IMSI, or Intracytoplasmic Morphologically Selected Sperm Injection, uses high-magnification microscopy to examine sperm closely. It selects the ones with the best shape for ICSI.
- Testicular Sperm Extraction (TESE) gets sperm straight from the testicles. This method usually has less DNA damage than sperm found in the semen.
- Electrophoresis: Separates sperm based on their electric charge, isolating high-quality sperm quickly.
Managing High DFI
Reversing DNA fragmentation is tough, but there are ways to minimize its effects:
- Lifestyle Changes: A healthy lifestyle can improve sperm health. This includes:
Eating a balanced diet with antioxidants
Exercising regularly
Avoiding smoking and too much alcohol
Managing your weight
- Antioxidant Supplements: These supplements can lower oxidative stress and improve sperm DNA health.
- Medical issues: Treating underlying conditions can help improve DFI. The conditions include infections, varicocele, and other medical issues.
- Surgical Sperm Retrieval: If a man has a very low sperm count or no sperm at all, doctors may retrieve sperm from the testes or epididymis. This method often results in sperm that have lower DNA fragmentation levels.
- Sperm Selection Techniques: Techniques like MACS and PICSI choose sperm with better DNA quality for ART.