Role of Stem Cells in Embryology and Regenerative Medicine
Stem cells in embryology are studied as part of embryology. Researchers have looked into various aspects of stem cells and how they affect the body system.
Stem cells as well as regenerative medicine do play a role in developmental biology, more so if the focus is on stem cells in embryology. How?
- Developmental biologists do tend to seek to uncover what genes and pathways are involved in cell differentiation and how these can be manipulated in order to create new healthy tissues.
- Stem cells can be applied to drug testing as well as development.
- Stem cell research programs do investigate the roles of adult and embryonic stem cells in normal development.
- Stem cells have more potential in regenerative therapies for kidney disease, eye disorders, as well as neural degeneration.
Regenerative medicine, which happens to be the most recent and also emerging branch of medical science, does deal with functional restoration of tissues or organs for patients suffering from severe injuries or even chronic diseases. The fantastic progress in the field of stem cell research has indeed laid the foundation for cell-based therapies for diseases that cannot really be cured by conventional medicines. The indefinite self-renewal as well as the potential to differentiate into other types of cells that represent stem cells are frontiers of regenerative medicine. Embryology does play an important role in this respect.
What are stem cells?
Stem cells happen to be the body’s raw materials, cells from which all other cells with specialized functions get generated. Under the proper conditions in the body or a laboratory, stem cells tend to divide to form more cells known as daughter cells.
These daughter cells do become either new stem cells or specialized cells (differentiation) with a more specific function, like blood cells, brain cells, heart muscle cells, or bone cells.
Researchers hope stem cell studies will help to:
- Increase understanding of how diseases occur.
- Generate healthy cells to replace cells affected by disease (regenerative medicine).
- Test new drugs for safety and effectiveness.
There are, in fact, several sources of stem cells:
- Embryonic stem cells.
- Adult stem cells.
- Adult cells have been altered to have the properties of embryonic stem cells.
- Perinatal stem cells.
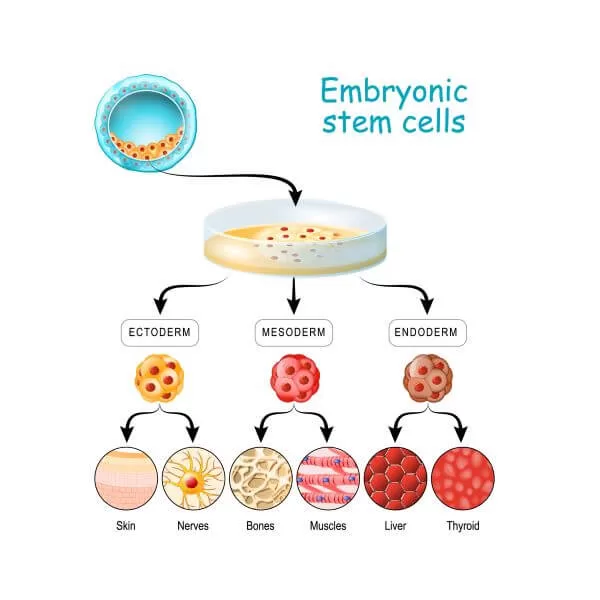
Embryonic stem cells are rather obtained from early-stage embryos—a group of cells that forms when eggs are fertilized with sperm at an in vitro fertilization clinic. As human embryonic stem cells are extracted from human embryos, several questions and issues have been raised about the ethics of embryonic stem cell research.
Where do these embryos come from?
The embryos being used in embryonic stem cell research are derived from eggs that were fertilized at in vitro fertilization clinics but never implanted in women’s uteruses. The stem cells are donated with no doubt informed consent from donors. The stem cells can live as well as grow in special solutions in existing test tubes or petri dishes in laboratories.
Why are researchers unable to use adult stem cells instead?
Although research into adult stem cells is quite promising, adult stem cells may not be as versatile and durable as embryonic stem cells. Adult stem cells may not be able to be manipulated in order to produce all cell types, which limits how adult stem cells can be used to treat diseases.
Adult stem cells are more likely to contain abnormalities on account of environmental hazards, like toxins, or from errors acquired by the cells during replication. Researchers have been able to find that adult stem cells are more adaptable.
Conclusion
Stem cells in embryology are part and parcel of embryology. Researchers have conducted much study into the composition and functioning of stem cells.
Write your message

